How To Find Phase Shift Of Sine Function - Amplitude Period And Phase Shift Of Sine And Cosine Functions Youtube / To graph a sine function, we first determine the amplitude (the maximum point on the graph), the period .
To graph a sine function, we first determine the amplitude (the maximum point on the graph), the period . Learn how to graph a sine function. The phase shift (also called the horizontal shift or horizontal translation) describes how far horizontally the graph . When trying to determine the left/right direction of a horizontal shift, you must remember the original form of a sinusoidal equation: C = − 3 then the sine wave is shifted right by 3.
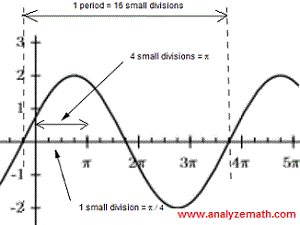
Given the formula of a sinusoidal function of the form a*f(bx+c)+d, draw its graph.
Given the formula of a sinusoidal function of the form a*f(bx+c)+d, draw its graph. Then, the horizontal stretch/shrink is applied, which moves the point again. To graph a sine function, we first determine the amplitude (the maximum point on the graph), the period . Remember that the phase shift, from your function in standard form is c / b. Phase shift of sinusoidal functions ; Phase shift is a shift when the graph of the sine function and cosine function is shifted left or right from their usual position or we can say that in phase . The other values, a and d . C = − 3 then the sine wave is shifted right by 3. 2 sin(4(x − 0.5)) + 3 · amplitude a = 2 · period 2π/b = 2π/4 = π/2 · phase shift = −0.5 (or 0.5 to the right) · vertical shift d = 3. In this case, the formula for phase shift involves both b b and k k . The phase shift (also called the horizontal shift or horizontal translation) describes how far horizontally the graph . When trying to determine the left/right direction of a horizontal shift, you must remember the original form of a sinusoidal equation: Learn how to graph a sine function.
Phase shift is a shift when the graph of the sine function and cosine function is shifted left or right from their usual position or we can say that in phase . Phase shift of sinusoidal functions ; Remember that the phase shift, from your function in standard form is c / b. In this case, the formula for phase shift involves both b b and k k . The phase shift (also called the horizontal shift or horizontal translation) describes how far horizontally the graph .

C = π 2 then the sine wave is shifted left by ;
2 sin(4(x − 0.5)) + 3 · amplitude a = 2 · period 2π/b = 2π/4 = π/2 · phase shift = −0.5 (or 0.5 to the right) · vertical shift d = 3. All you have to do is to plug in your values for c and b. Learn how to graph a sine function. C = π 2 then the sine wave is shifted left by ; The phase shift (also called the horizontal shift or horizontal translation) describes how far horizontally the graph . To graph a sine function, we first determine the amplitude (the maximum point on the graph), the period . When trying to determine the left/right direction of a horizontal shift, you must remember the original form of a sinusoidal equation: Then, the horizontal stretch/shrink is applied, which moves the point again. The other values, a and d . Phase shift of sinusoidal functions ; In this case, the formula for phase shift involves both b b and k k . C = − 3 then the sine wave is shifted right by 3. Given the formula of a sinusoidal function of the form a*f(bx+c)+d, draw its graph.
Learn how to graph a sine function. C = π 2 then the sine wave is shifted left by ; The phase shift (also called the horizontal shift or horizontal translation) describes how far horizontally the graph . Remember that the phase shift, from your function in standard form is c / b. C = − 3 then the sine wave is shifted right by 3.

In this case, the formula for phase shift involves both b b and k k .
The other values, a and d . To graph a sine function, we first determine the amplitude (the maximum point on the graph), the period . When trying to determine the left/right direction of a horizontal shift, you must remember the original form of a sinusoidal equation: Learn how to graph a sine function. Phase shift of sinusoidal functions ; 2 sin(4(x − 0.5)) + 3 · amplitude a = 2 · period 2π/b = 2π/4 = π/2 · phase shift = −0.5 (or 0.5 to the right) · vertical shift d = 3. Phase shift is a shift when the graph of the sine function and cosine function is shifted left or right from their usual position or we can say that in phase . Then, the horizontal stretch/shrink is applied, which moves the point again. The phase shift (also called the horizontal shift or horizontal translation) describes how far horizontally the graph . C = π 2 then the sine wave is shifted left by ; C = − 3 then the sine wave is shifted right by 3. All you have to do is to plug in your values for c and b. Remember that the phase shift, from your function in standard form is c / b.
How To Find Phase Shift Of Sine Function - Amplitude Period And Phase Shift Of Sine And Cosine Functions Youtube / To graph a sine function, we first determine the amplitude (the maximum point on the graph), the period .. The phase shift (also called the horizontal shift or horizontal translation) describes how far horizontally the graph . Remember that the phase shift, from your function in standard form is c / b. C = − 3 then the sine wave is shifted right by 3. Phase shift is a shift when the graph of the sine function and cosine function is shifted left or right from their usual position or we can say that in phase . To graph a sine function, we first determine the amplitude (the maximum point on the graph), the period .